What is Conversational AI and How Does it Work?
March 2025
Conversational artificial intelligence (CAI) solutions use AI and generative AI (GenAI) technologies to identify, understand, and respond to customer conversation intents. CAI applications enable consumers to self-serve or can assist live agents responding to customer inquiries. These omnichannel and multimodal platforms leverage large volumes of data, machine learning, natural language processing (NLP)/understanding (NLU)/generation (NLG), cognitive search, and GenAI to recognize and respond to customer inputs in a way that mimics human conversation. CAI solutions are designed to support free-flow dialogues in which consumers speak naturally, using their own words, to make requests. These applications deliver a persistent and consistent user experience across all touchpoints to reduce customer effort and enhance the customer experience (CX) while increasing self-service automation.
Conversational AI self-service solutions allow an enterprise’s customers to obtain information and answers to questions, track order status, complete transactions, purchase new products, schedule appointments, etc., without the help of a live agent, salesperson, or other employee. Unlike rules-based self-service applications, including interactive voice response (IVR) systems and early-generation intelligent virtual agents (IVAs), CAI solutions utilize multiple native and/or third-party AI and GenAI technologies, including large language models (LLMs), to understand intents in natural language conversations and deliver accurate and relevant responses without live agent assistance. However, like all solutions leveraging LLM-based GenAI, adequate guardrails are required to ensure they stay within appropriate guidelines and do not get creative and hallucinate. When a CAI solution doesn’t know how to handle a request, it is escalated to its human counterparts, along with customer and interaction data to provide background and context as part of the hand-off process.
Self-Service: GenAI-Enabled Conversational AI Solutions
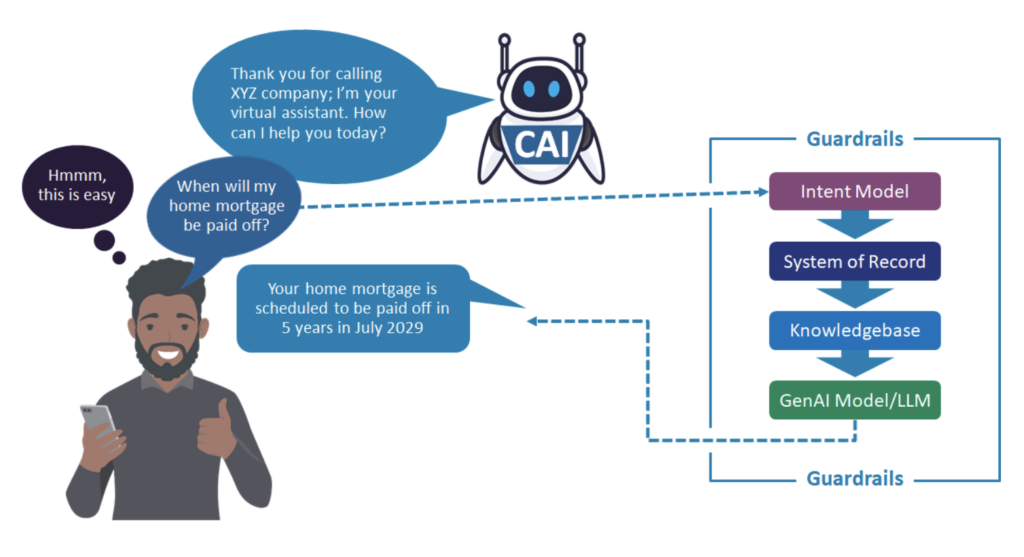
Source: DMG Consulting LLC, March 2025
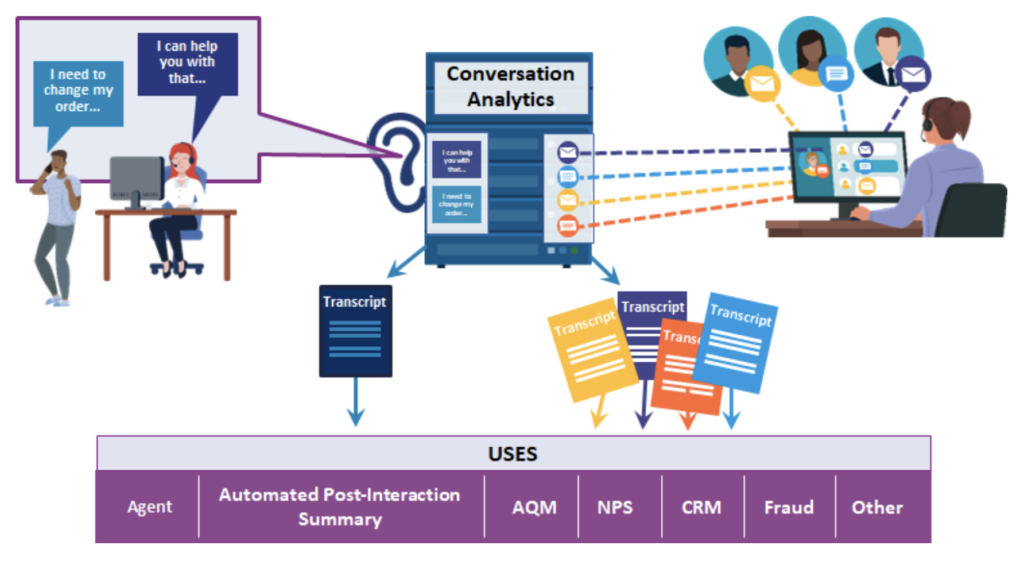
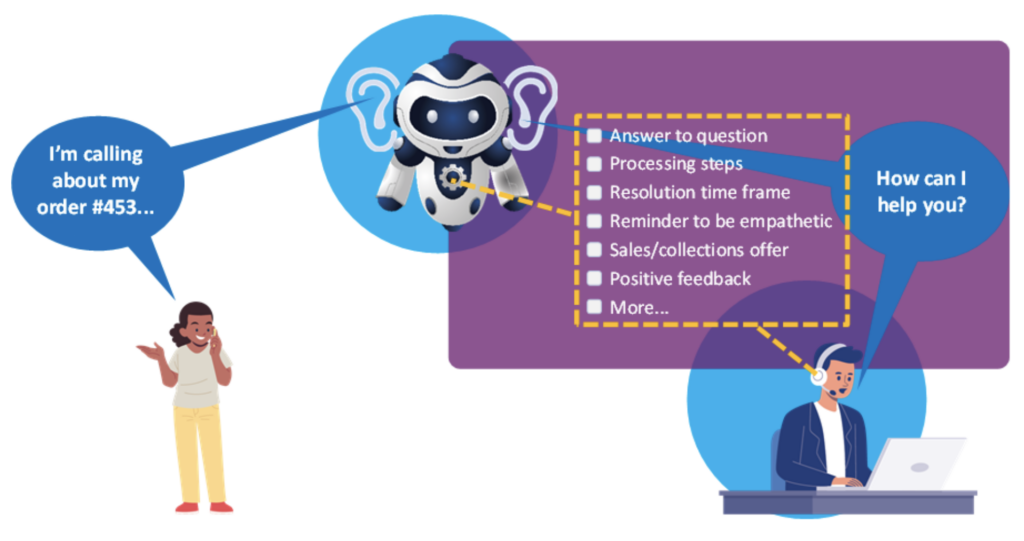
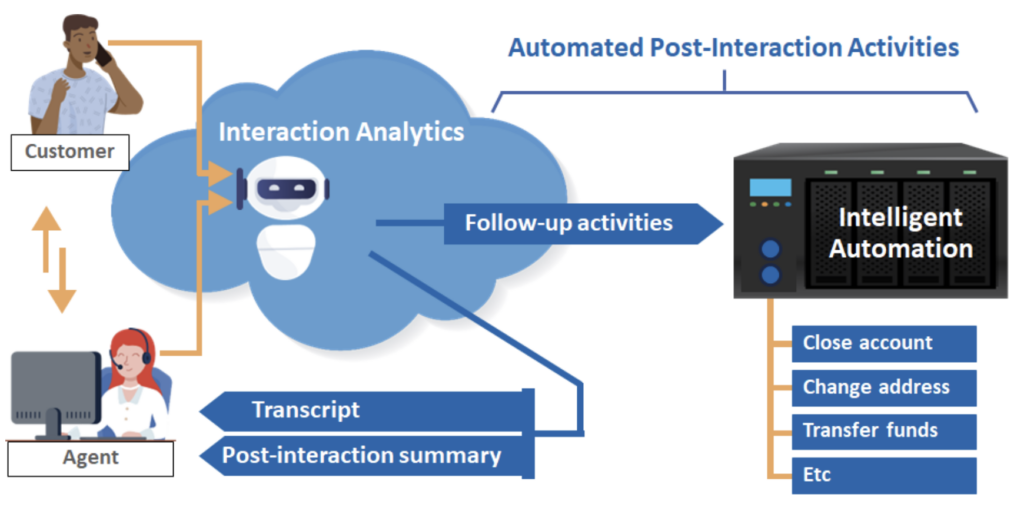
Many CAI solutions started as customer-facing self-service applications; however, emerging CAI platforms also deliver agent assist tools to augment employee performance. The idea is that if CAI solutions can identify and understand intents to enable customers to help themselves, this understanding can also be leveraged to source and deliver context-relevant content and responses to agents. This frees agents to spend their time helping customers instead of looking for information, policies, or knowledge articles to answer questions, thus improving the customer and agent experience. Agent assist applications include transcription, real-time guidance (RTG)/next-best-action (NBA), and automated post-interaction summarization.
Agent Assist Applications
Transcription
Real-Time Guidance
Automated Post-Interaction Summarization
Source: DMG Consulting LLC, March 2025
While each of the agent assist tools has been in the market in one form or another for a few years, GenAI has already greatly improved their accuracy and effectiveness and is delivering quantifiable benefits to users. As an example, automated post-interaction summarization applications reduce the wrap-up process by an average of 25% – 40%, while vastly enhancing the clarity and usefulness of the documentation. But this is just the beginning for these solutions. The next step, which is already finding its way to market, is using them to identify interaction follow-up activities and automating the resolution process to close the loop.
Final Thoughts
GenAI-enhanced CAI solutions are the future of self-service because of their ability to understand a wide range of intents and generate appropriate responses. The potential and power of these applications is extremely broad, which is why they need to be directed to appropriate data sources and restricted by guardrails. As these solutions are feature-rich, omnichannel, and multimodal by design, they can be leveraged for both customer- and agent-facing activities and deliver significant benefits to both user groups.
